I often find myself in a situation where I need to create bootable Windows USBs which I have found to be a very daunting task on Linux as most of the tools out there tend to be unreliable. My solution to this problem is to do it manually and write script to automate it so that its consistent and repeatable.
The Theory and Test build
These are the general steps that required to successfully create a Windows USB:
- Create partition table on drive as type 7 and bootable
- Format drive as NTFS
- Write Master Boot Record to drive
- Mount ISO image
- Mount USB device
- Transfer files from ISO to USB device
I first set out to accomplish these tasks one by one and write a script to automate it:
#!/bin/bash
# runs cfdisk for second command argument
cfdisk $2
# create NTFS partition on storage device
mkfs.ntfs -f ${2}1
# write master boot record to device
dd if=/usr/share/syslinux/mbr.bin of=$1
# create mountpoint directories
mkdir -v /tmp/iso /tmp/usb
# mount iso image
mount -vo loop $1 /tmp/iso
# mount usb device
mount -v $2 /tmp/usb
# transfer files from iso image to usb device
rsync -Prv /tmp/iso/ /tmp/usb
# sync cached data to storage device
sync -f /tmp/usb
# unmount iso image
umount -v $1
# unmount usb device
umount -v $2
# removes mountpoint directories
rmdir /tmp/iso /tmp/usb
So thats it, it works right? Yes but he main issue with this is that it expects everything to be correct before the script is ran and doesn’t account for errors and I can do better.
Writing the Script
As it is required to mount devices the first obvious thing to check for is if the script it actually being ran as the root user:
if [[ $(id -u) -ne 0 ]]; then
echo "Script must be ran as root"
exit 1
fi
and if any arguments are being passed to the script:
if [[ -z $1 || -z $2 ]]; then
echo "Specify path to iso image and usb device: $0 /path/to/iso /dev/sdX"
exit 1
fi
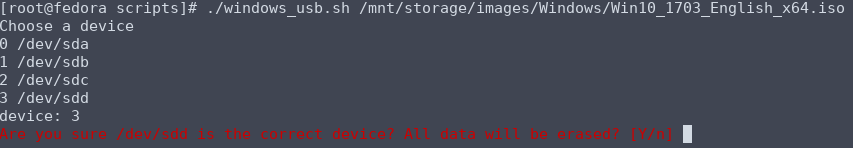
I then decided that I wanted to make a rudimentary UI for selecting the storage device as it was something I could automate easily:
# get list of storage devices from lsblk
disks=($(lsblk -dnp --output NAME))
echo "Choose a device"
# loops through and echos storage devices
for i in "${!disks[@]}"; do
echo "$i ${disks[$i]}"
done
# user input for storage device
read -p "device: " i
# warning for selected storage device
echo -ne "\e[0;31mAre you sure ${disks[$i]} is the correct device? All data will be erased? [Y/n] \033[0m"
read go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
# do some stuff
else
exit 1
fi
The UI works by looping through a list of storage devices taken from lsblk and asks the user to select a device by its given number and displays a warning message asking for confirmation:
With the UI in place I set out to do a check to if the partition on the device was mounted and and direct the user to unmount it or exit the script:
device=/dev/${disks[$i]}
# checks if a partition is mounted
if [ -n "$(mount | grep $device)" ]; then
# asks user if they want to unmount the partition
read -p "A partition is mounted on $device, do you want to umount it? [Y/n] " check
if [[ ${check,,} = "y" ]]; then
# unmount partition
umount ${device}1
else
exit 1
fi
fi
I then did a check asking the user if they wanted a create the partition table on the device and if not exit the script.
# asks the user to create partition table
echo -e "Create partition table on $device (Select partition \033[1mtype 7\033[0m and \033[1mbootable\033[0m flag)"
read -p "contiune [Y/n]: " go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
# runs cfdisk for selected storage device
cfdisk $device
// do some more stuff
else
exit 1
fi
It was at this point that I noticed pattern in that the script exits every time it gets an undesirable result which could be annoying for the user, so to fix this I decided to enclose the main logic of the script inside a while loop:
# main while loop
while true; do
# get list of storage devices from lsblk
disks=($(lsblk -dnp --output NAME))
echo "Choose a device"
for i in "${!disks[@]}"; do
echo "$i ${disks[$i]}"
done
# user input for storage device
read -p "device: " i
# warning for selected storage device
echo -e "\e[0;31mAre you sure /dev/${disks[$i]} is the correct device? All data will be erased? [Y/n] \033[0m"
read go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
device=/dev/${disks[$i]}
# checks if a partition is mounted
if [ -n "$(mount | grep $device)" ]; then
# asks user if they want to unmount the partition
read -p "A partition is mounted on $device, do you want to umount it? [Y/n] " check
if [[ ${check,,} = "y" ]]; then
# unmount partition
umount ${device}1
else
# continue while loop
continue
fi
fi
# asks the user to create partition table
echo -e "Create partition table on $device (Select partition \033[1mtype 7\033[0m and \033[1mbootable\033[0m flag)"
read -p "contiune [Y/n]: " go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
# runs cfdisk for selected storage device
cfdisk $device
# break from while loop
break
else
# continue while loop
continue
fi
fi
done
In here all the logic is the same except that exit is replaced with continue which will loop back to the beginning of the user interface and a break after the partition table has been created with cfdisk.
With the main logic for preparing the storage device done I now focused on creating the bootable USB. This section is mostly the same as the original code except for extra checking for the mountpoints and whether syslinux/mbr.bin exists (Thanks @Dje4321 suggesting that).
# create NTFS partition on storage device
mkfs.ntfs -f ${device}1
# path to mbr.bin
mbr="/usr/share/syslinux/mbr.bin"
# checks if mbr.bin exists
if [ -f $mbr ]; then
# write mbr to storage device
dd if=$mbr of=$device
else
# echos error and exits
echo "Error: $mbr could not be found"
exit 1
fi
# mountpoints for iso image and storage device
mounts=("/tmp/iso" "/tmp/usb")
# loops through $mounts
for i in "${!mounts[@]}"; do
# checks if directories for mounts don't exist
if [ ! -d ${mounts[$i]} ]; then
# creates directories for iso image and storage device
mkdir -v ${mounts[$i]}
fi
done
# mounts iso image
mount -vo loop $1 ${mounts[0]}
# mounts storage device
mount -v ${device}1 ${mounts[1]}
# rsync data from iso image to storage device
rsync -Prv ${mounts[0]}/ ${mounts[1]}
echo "Syncing device, This could take a while."
# sync cached data to storage device
sync -f ${mounts[1]}
echo "Cleaning up..."
# loops through $mounts
for i in "${!mounts[@]}"; do
# unmount iso image and storage device
umount -v ${mounts[$i]}
# removes mountpoint directories
rmdir ${mounts[$i]}
done
Further Improvements
With that the main program is done but there were some slight improvements I made to the main while loop to make it more robust and improve the UI:
- It now loops through every partition on the device and directs the user to unmount it.
- More checking to see if a device is busy before unmounting
- Minor visual improvements in the UI
# main while loop
while true; do
# get list of storage devices from lsblk
disks=($(lsblk -dnp --output NAME))
echo "Choose a device"
# loops through and echos storage devices
for i in "${!disks[@]}"; do
echo "$i ${disks[$i]}"
done
# user input for storage device
read -p "device: " i
# warning for selected storage device
echo -ne "\e[0;31mAre you sure ${disks[$i]} is the correct device? All data will be erased? [Y/n] \033[0m"
read go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
device=${disks[$i]}
# stores list of partitions for the selected storage device
partitions=($(lsblk $device -fnpr --output NAME | sed -n '1!p'))
# loops through partitions
for i in "${!partitions[@]}"; do
# stores the mountpoint for partitions
mountpoint=$(lsblk ${partitions[$i]} -dn --output MOUNTPOINT)
# checks if a partition is mounted
if [ -n "$(mount | grep ${partitions[$i]})" ]; then
# asks user if they want to unmount the partition
read -p "${partitions[$i]} is mounted on $mountpoint do you want to unmount it? [Y/n] " check
if [[ ${check,,} = "y" ]]; then
# checks if partition is busy
if [ -n "$(fuser $mountpoint)" ]; then
echo "$mountpoint: target is busy"
# continue while loop
continue 2
else
# unmount partition
umount -v $mountpoint
fi
else
# continues while loop if user doesn't want to unmount the partition
continue 2
fi
fi
done
# asks the user to create partition table
echo -e "Create partition table on $device (Select partition \033[1mtype 7\033[0m and \033[1mbootable\033[0m flag)"
read -p "contiune [Y/n]: " go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
# runs cfdisk for selected storage device
cfdisk $device
# break from while loop
break
else
# continues while loop if user selects no
continue
fi
fi
done
Things that went wrong
There were a couple of setbacks when writing this, mainly around cleanly unmounting the storage device after the script has finished. I originally wrote it to not include the sync -f option after the file transfer but this resulted in the program either hanging or throwing errors when unmounting the device. With the sync -f option this is resolved but particularly on usb flash drives can take a very long time to complete. I am open to any suggestions on improving this or making the file transfer more efficient.
Completed Script
#!/bin/bash
# path to mbr.bin
mbr="/usr/share/syslinux/mbr.bin"
# mountpoints for iso image and storage device
mounts=("/tmp/iso" "/tmp/usb")
# check to if the script is ran as root
if [[ $(id -u) -ne 0 ]]; then echo "Script must be ran as root"; exit 1; fi
# checks for iso image argument
if [[ -z $1 ]]; then echo "Specify path to iso image: $0 /path/to/iso"; exit 1; fi
# main while loop
while true; do
# get list of storage devices from lsblk
disks=($(lsblk -dnp --output NAME))
echo "Choose a device"
# loops through and echos storage devices
for i in "${!disks[@]}"; do
echo "$i ${disks[$i]}"
done
# user input for storage device
read -p "device: " i
# warning for selected storage device
echo -ne "\e[0;31mAre you sure ${disks[$i]} is the correct device? All data will be erased? [Y/n] \033[0m"
read go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
device=${disks[$i]}
# stores list of partitions for the selected storage device
partitions=($(lsblk $device -fnpr --output NAME | sed -n '1!p'))
# loops through partitions
for i in "${!partitions[@]}"; do
# stores the mountpoint for partitions
mountpoint=$(lsblk ${partitions[$i]} -dn --output MOUNTPOINT)
# checks if a partition is mounted
if [ -n "$(mount | grep ${partitions[$i]})" ]; then
# asks user if they want to unmount the partition
read -p "${partitions[$i]} is mounted on $mountpoint do you want to unmount it? [Y/n] " check
if [[ ${check,,} = "y" ]]; then
# checks if partition is busy
if [ -n "$(fuser $mountpoint)" ]; then
echo "$mountpoint: target is busy"
# continue while loop
continue 2
else
# unmount partition
umount -v $mountpoint
fi
else
# continues while loop if user doesn't want to unmount the partition
continue 2
fi
fi
done
# asks the user to create partition table
echo -e "Create partition table on $device (Select partition \033[1mtype 7\033[0m and \033[1mbootable\033[0m flag)"
read -p "contiune [Y/n]: " go
if [[ ${go,,} = "y" ]]; then
# runs cfdisk for selected storage device
cfdisk $device
# break from while loop
break
else
# continues while loop if user selects no
continue
fi
fi
done
# create NTFS partition on storage device
mkfs.ntfs -f ${device}1
# checks if mbr.bin exists
if [ -f $mbr ]; then
# write mbr to storage device
dd if=$mbr of=$device
else
# echos error and exits
echo "Error: $mbr could not be found"
exit 1
fi
# loops through $mounts
for i in "${!mounts[@]}"; do
# checks if directories for mounts don't exist
if [ ! -d ${mounts[$i]} ]; then
# creates directories for iso image and storage device
mkdir -v ${mounts[$i]}
fi
done
# mounts iso image
mount -vo loop $1 ${mounts[0]}
# mounts storage device
mount -v ${device}1 ${mounts[1]}
# rsync data from iso image to storage device
rsync -Prv ${mounts[0]}/ ${mounts[1]}
echo "Syncing device, This could take a while."
# sync cached data to storage device
sync -f ${mounts[1]}
echo "Cleaning up..."
# loops through $mounts
for i in "${!mounts[@]}"; do
# unmount iso image and storage device
umount -v ${mounts[$i]}
# removes mountpoint directories
rmdir ${mounts[$i]}
done
Git repositories for the script can be found on either Github or Bitbucket here: